| Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, ISSN 1923-2861 print, 1923-287X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Endocrinol Metab and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jofem.org |
Letter to the Editor
Volume 7, Number 6, December 2017, pages 197-198
Practical Diagnostic Algorithm for Pituitary Tumors: What Is New in the 2017 WHO Classification?
Francisco Tortosaa, b, c
aInstituto de Anatomia Patologica, Faculdade de Medicina, Universidade de Lisboa, Avenida Professor Egas Moniz, 1649-028 Lisbon, Portugal
bDepartment of Medicine/Endocrinology, Hospital Sant Pau. Universitat Autonoma de Barcelona (UAB), Pare Claret, 167. 08025 Barcelona, Spain
cCorresponding Author: Francisco Tortosa, Instituto de Anatomia Patologica, Faculdade de Medicina, Universidade de Lisboa, Avenida Professor Egas Moniz, 1649-028 Lisbon, Portugal
Manuscript submitted December 10, 2017, accepted December 20, 2017
Short title: Diagnostic Algorithm for Pituitary Tumors
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jem476w
| To the Editor | ▴Top |
In the new edition of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of tumors of the pituitary gland, major changes are recommended [1]. Pituitary adenoma (PA) classification has changed regarding aggressive lesions. The aim of this paper was to provide a clear and simple update of the main recommended changes, especially for professionals in direct contact with such pathology, with an objective, practical and easy to use diagnostic algorithm that includes a novel approach for classifying pituitary tumors.
A major change in the new WHO classification is the adoption of a pituitary adenohypophyseal cell lineage as the main principle guiding the classification of adenomas: the acidophilic lineage (with the transcription factor PIT1), the corticotroph lineage (with TPIT), and the gonadotroph lineage (with SF1) [2]. With this novel concept, the 2017 WHO classification organizes adenomas according to their pituitary cell lineage rather than according to a hormone-producing PA (now named as lactotroph adenomas, somatotroph adenomas, thyrotroph adenomas, corticotroph adenomas, gonadotroph adenomas, and null-cell adenomas, adenomas for which the cell lineage is yet not determined; specific subclassification in morphological variants is determined according to specific histological and immunohistochemical features). Electron microscopy is now very rarely used to classify pituitary tumors [3].
Null-cell adenomas are now defined by the 2017 WHO classification as tumors that have no immunohistochemical evidence of cell-type-specific differentiation by using adenohypophyseal hormones and pituitary transcription factors. These tumors should be considered a diagnosis of exclusion from other rare neuroendocrine tumors that can present in the sellar region.
In the new WHO classification, the term “atypical adenoma” is abandoned [3], and emphasis is placed on the evaluation of tumor proliferation (mitotic count and Ki-67 index - no cutoff value is recommended), in tumor invasion, and in special variants of adenomas for which clinical behavior has been shown to be more aggressive due to their intrinsic histological features (lactotroph adenoma in men, sparsely granulated somatotroph adenoma, the silent corticotroph adenoma, the Crooke’s cell adenoma - a corticotroph adenoma variant composed in > 60% of cells with ring-like deposition of cytokeratin called Crooke’s change - and the plurihormonal PIT1-positive adenoma -previously known as silent subtype III pituitary adenoma) [4].
Similar to the guidelines of the revised fourth edition of the WHO classification of tumors of the CNS, the thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF1) serves as an immunomarker for the diagnosis of tumors derived from the posterior pituitary gland (including the pituicytoma, the granular cell tumor of the neurohypophysis, and the spindle cell oncocytoma) with strong nuclear immunoreactivity.
A new entity recognized by the 2017 classification is the pituitary blastoma, a rare primitive malignant neoplasm of the pituitary gland that occurs mostly in infants younger, histologically composed of three main elements including epithelial glands with rosette-like formations resembling immature Rathke epithelium, small primitive appearing cells with a blastema-like appearance, and larger secretory epithelial cells resembling adenohypophyseal cells [5].
A flow chart of the most common pituitary tumors including some cell differentiation IHC markers and prognostic markers is shown in the Figure 1. It is hoped that this new algorithm may help practicing pathologists to better diagnose these tumors.
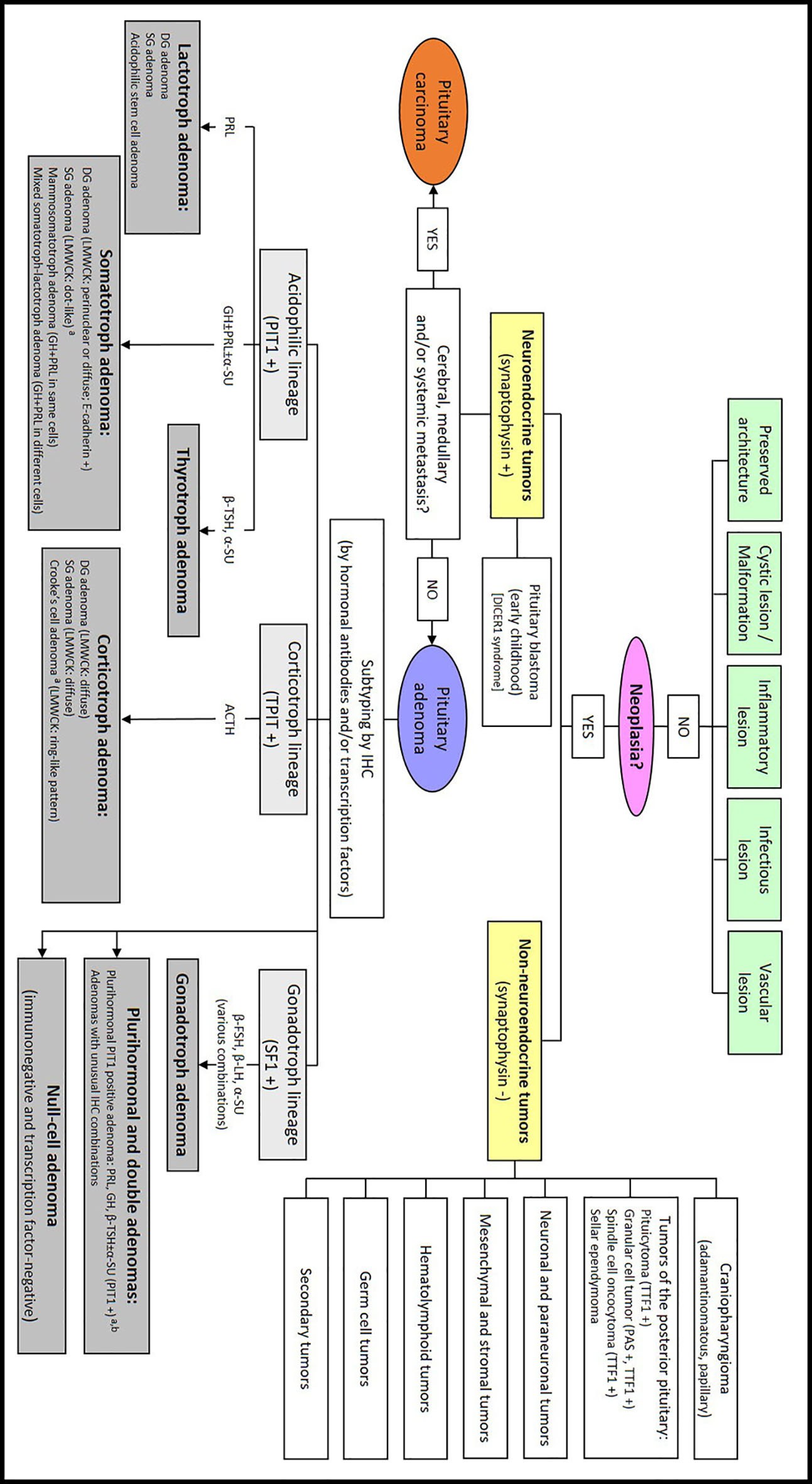 Click for large image | Figure 1. New practical approach to diagnostic pituitary pathology. ACTH: adrenocorticotropic hormone; α-SU: alpha-subunit; β-FSH: follicle-stimulating hormone subunit beta; β-LH: luteinizing hormone subunit beta; β-TSH: thyroid-stimulating hormone subunit beta; DG: densely granulated; GH: growth hormone; IHC: immunohistochemistry; LMWCK: low-molecular-weight cytokeratin; PAS: periodic acid Schiff; PIT1: pituitary-specific POU-class homeodomain transcription factor 1; PRL: prolactin; SF1: steroidogenic factor 1; SG: sparsely granulated; TPIT: T-box family member TBX19; TTF1: thyroid transcription factor 1. aAdenomas associated with an elevated risk for recurrence. Clinically aggressive adenomas: high mitotic index; high Ki-67; tumor invasion. bPreviously called silent subtype 3 adenoma. |
Conflict of Interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest concerning this article.
| References | ▴Top |
- Lloyd RV, Osamura RY, Kloppel G, Rosai J. WHO classification of tumours of endocrine organs, fourth ed. Lyon: IARC Press, 2017.
- Zhu X, Rosenfeld MG. Transcriptional control of precursor proliferation in the early phases of pituitary development. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004;14(5):567-574.
doi pubmed - Osamura RY, Lopes MBS, Grossman A, Kontogeorgos G, Trouillas J. Introduction. In: Lloyd RV, Osamura RY, Kloppel G, Rosai J, eds. WHO classification of tumours of endocrine organs. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press, 2017: p. 15.
- Mete O, Lopes MB. Overview of the 2017 WHO Classification of Pituitary Tumors. Endocr Pathol. 2017;28(3):228-243.
doi pubmed - Scheithauer BW, Horvath E, Abel TW, Robital Y, Park SH, Osamura RY, Deal C, et al. Pituitary blastoma: a unique embryonal tumor. Pituitary. 2012;15(3):365-373.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism is published by Elmer Press Inc.
