| Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, ISSN 1923-2861 print, 1923-287X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Endocrinol Metab and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jofem.org |
Case Report
Volume 2, Number 3, June 2012, pages 151-153
Unusual Intravenous Application of Insulin in a Case of Patient With Juvenile Diabetes and Subcutaneous Insulin Resistance
Sebastian Koballa, c, Michael Hinza, Heiko Hicksteinb
aUniversity of Rostock, Department of Internal Medicine, Nephrology, Germany
bKuratorium fur Heimdialyse Wismar, Germany
cCorresponding author: Sebastian Koball, University of Rostock, Department of Internal Medicine, Nephrology, Ernst-Heydemann-Street 6, 18055 Rostock, Germany
Manuscript accepted for publication April 6, 2012
Short title: Insulin in Subcutaneous Insulin Resistance
doi: https://doi.org/10.4021/jem85w
| Abstract | ▴Top |
A 44 years old female patient suffering from juvenile diabetes, showed a subcutaneous insulin resistance. Intravenous insulin application was the therapy of choice. Due to various problems of vascular access (mainly thrombosis and infectious problems) an arterio venous shunt was implemented as a last choice. Repeated puncture and insertion of common butterfly canule led to a gnarled transformation of the used vessel. The risk of thrombosis and failing of the vascular access was evident. In the absence of alternatives we tried injection systems for subcutaneous insulin application. The advantage of these systems is lower diameters and more flexible materials, suggesting higher biocompatibility. During this therapy the gnarled transformation decreased, the blood flow in the vascular shunt improved. The use of the small (subcutaneous) infusion systems for intravascular application of insulin showed that to be a save alternative in this case.
Keywords: Subcutaneous insulin resistance; Vascular access; Insulin pump; Arterio venous shunt
| History and Examination | ▴Top |
The patient was a 44 years old female with a juvenile diabetes mellitus. Due to Type I of diabetes mellitus insulin treatment was started immediately. After the first 6 month of uncomplicated subcutaneous insulin treatment a subcutaneous insulin resistance occurred.
Starting intravenous insulin application with a common butterfly needle was the result. Insulin was administered continuously using a pump. After infectious problems a peritoneal katheter for insulin administration was initiated. The katheter has been removed due to ineffective insulin adsorption after 3 months. In the following several subclavian port systems were implanted and showed shortly after implantation a dysfunction due to thrombotic problems. Because of these problems a pancreas transplantation was performed in august 2004. The pancreas transplant has been removed in February 2005 due to chronic allograft rejection. A new course of subclavian access with the same problems was started, also a second try with a peritoneal catheter was performed. The second pancreas transplantation has been performed in December 2005, leading again to a chronic allograft rejection. The pancreas transplant was removed in July 2006. Because of obturation of subclavian and femoral veins a port system was implanted into the ovarian veins. This had to be also removed due to thrombotic obturation.
Extensive diagnostic of coagulation disorders showed no pathological results. Thrombosis only occurred in venous vessel with artificial vascular access.
Next an arterio venous shunt at the right thigh was implemented. This shunt was punctured with a butterfly canule and insulin application was performed using a pump (Pega plus, Venner Medical GmbH, Kiel, Germany). This was necessary because of flow rates and volume needed in the case of using a 22 gauge butterfly canule (outside radius 0.9 mm, inside radius 0.6 mm). This was successful for 20 months, repeated thrombosis were treated with thrombectomy. A shunt infection with shunt rupture resulting in a hemorrhagic shock ended this trial. An arterio venous shunt on the right upper arm was initiated. Already after first punctures the shunt showed a gnarled transformation with recurrent thrombosis. In the following 3 months thrombectomy and percutaneous transluminal angioplasties were performed repeatedly. A new arterio venous shunt at the left arm was implemented.
The shunt was punctured with a 22 gauge butterfly canula twice a week, insulin was continuously infused using a Pega plus pump (Venner Medical GmbH, Kiel, Germany). This was necessary because of pressure alarms using a common insulin pump and clotting problems.
Already in the first 4 weeks of treatment new tubercular changes of the shunt vein occured (see Fig. 1). These stenosis are risky for thrombosis and occurred corresponding to the puncture point as a reaction to the artificial material of the butterfly canule. We searched for a less traumatic kind of vascular access and tried the Accu-Chek TenderLink system (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany).
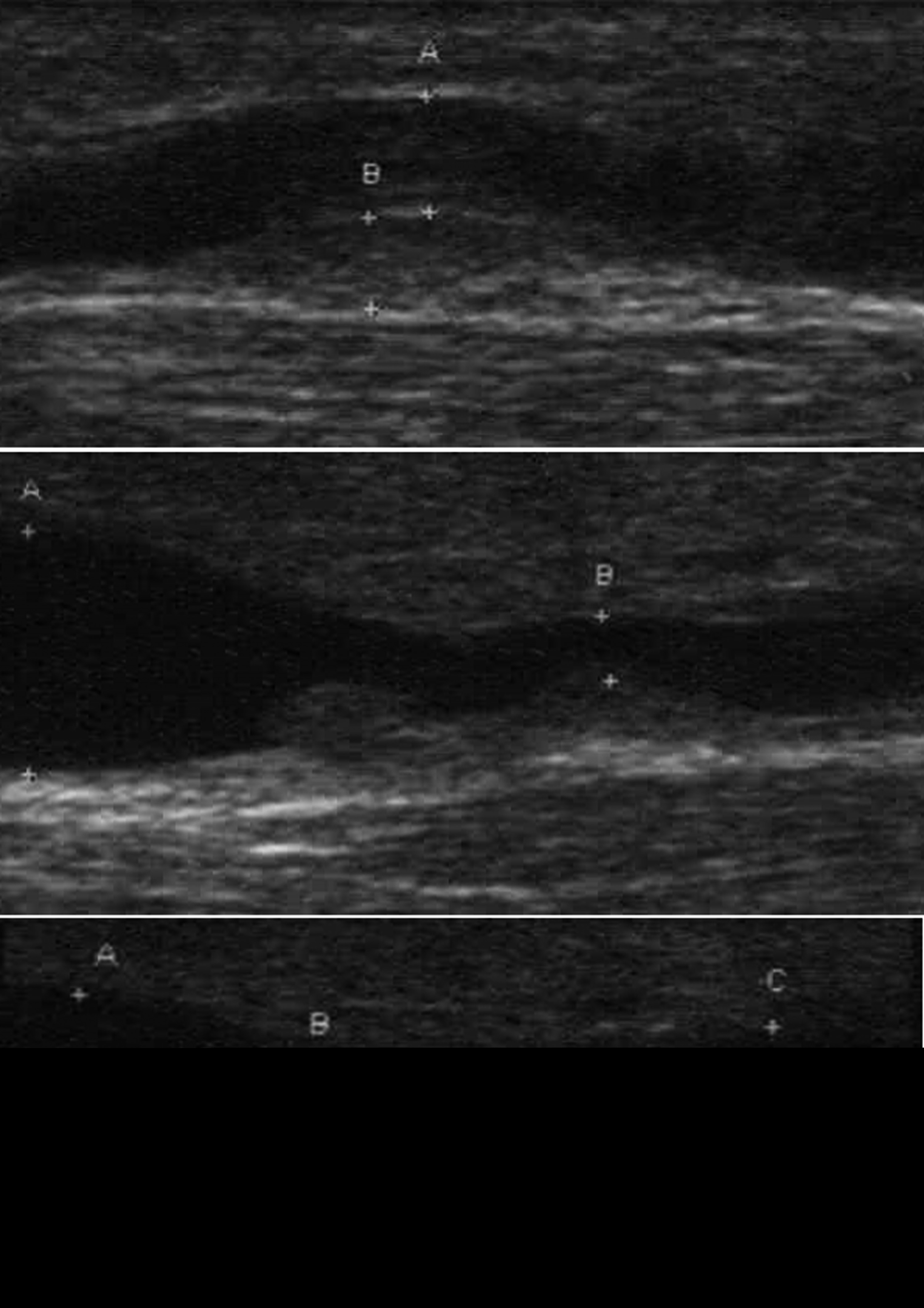 Click for large image | Figure 1. Multiple in shunt stenosis with fresh thrombotic material. |
The accuse check tender is for subcutaneous use only and consist of a 0.5 mm teflon canule, which is more flexible than other butterfly canules. Puncture was continued twice a week, 6 months after starting with the TenderLink system no problems occurred. There is no evidence for thrombotic problems. Ultrasonic control of the vessel showed regression of gnarled transfomation. The blood sugar level was very good (3.5 to 6.0 mmol/L). With the TenderLink system it was now possible to use a normal insulin pump (Accu Check spirit, Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany). The advantage of this pump as a special insulin pump is the possibility of giving an insulin bolus or programming of different basal rates. The better options for connecting or disconnecting the pump from the vascular access and the lower profile of this canule are also a good for patient satisfaction.
| Investigations | ▴Top |
Subcutaneous insulin resistance is a rare complication in the treatment of patients with a diabetes mellitus [1, 2]. It is characterized by resistance to subcutaneous insulin with normal response to intravenous insulin. The exact pathophysiology is unknown, an increased insulin degrading activity has been suggested [3] and also an impaired resorption of subcutaneous applicated insulin has been discussed.
The intraperitoneal [4] or intravenous insulin administration are usual capabilities. The venous application is often performed using port systems. Infections and thrombosis are common problems. Furthermore pancreas transplantation is the therapy of choice.
In our case all these common therapy options have failed. The institution of arterial vascular accesses is known and showed good usability in chronic dialysis patients. Continues vascular access with synthetic material is connected with endothelial reaction and risk of thrombosis. The need of long time vascular access led to the wastage of suitable vessels. Searching for a more biocompatible version for the insertion into the vessel we tried the above mentioned setting. Despite the fact that the use of this system is off label use, it seemed to be an alternative avoiding endothelial irritation with complications. The smooth material and the small diameter of the system for subcutaneous application of insulin are fitting these criterias and should be useable for the application of insulin. The relative fast decrease of gnarled transformation in the used vessels was unexpected but delightful. The intravenous insulin treatment of the patient in this case was save, effective and well tolerated by the patient. The approval of these systems should be extended to the intravascular use in special cases. First reports of inhaled insulin show this as an alternative treatment [5].
Conclusions
Subcutaneous insulin resistance is a rarely observed complication in the treatment of patients with diabetes mellitus. The need of intravascular application of insulin led often to infectious or thrombotic problems. More biocompatible alternatives for the vascular access are needed. The use of subcutaneous insulin application systems seems to be an alternative. The delineated case shows a save and effective treatment option in patients with no other choice.
Competing Interests
All authors declare that the answer to the questions on your competing interest form are all No and therefore have nothing to declare.
| References | ▴Top |
- Paulsen EP, Courtney JW, 3rd, Duckworth WC. Insulin resistance caused by massive degradation of subcutaneous insulin. Diabetes. 1979;28(7):640-645.
pubmed doi - Riveline JP, Vantyghem MC, Fermon C, Brunet C, Gautier JF, Renard E, Charpentier G. Subcutaneous insulin resistance successfully circumvented on long term by peritoneal insulin delivery from an implantable pump in four diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab. 2005;31(5):496-498.
pubmed doi - Schade DS, Duckworth WC. In search of the subcutaneous-insulin-resistance syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1986;315(3):147-153.
pubmed doi - Soudan B, Girardot C, Fermon C, Verlet E, Pattou F, Vantyghem MC. Extreme subcutaneous insulin resistance: a misunderstood syndrome. Diabetes Metab. 2003;29(5):539-546.
pubmed doi - van Alfen-van der Velden AA, Noordam C, de Galan BE, Hoorweg-Nijman JJ, Voorhoeve PG, Westerlaken C. Successful treatment of severe subcutaneous insulin resistance with inhaled insulin therapy. Pediatr Diabetes. 2010;11(6):380-382.
pubmed doi
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism is published by Elmer Press Inc.
