| Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, ISSN 1923-2861 print, 1923-287X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Endocrinol Metab and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jofem.org |
Letter to the Editor
Volume 1, Number 5, December 2011, pages 234-236
The Treatment for Anti-insulin Antibody-mediated Immunological Insulin Resistance
Hidekatsu Yanaia, b, c, Hiroki Adachia, Hidetaka Hamasakia, Shuichi Mishimaa
aDepartment of Internal Medicine, National Center for Global Health and Medicine, Kohnodai Hospital, Chiba 272-8516, Japan
bClinical Research Center, National Center for Global Health and Medicine, Kohnodai Hospital, Chiba 272-8516, Japan
cCorresponding author: Hidekatsu Yanai, Department of Internal Medicine, National Center for Global Health and Medicine, Kohnodai Hospital, 1-7-1 Kohnodai, Chiba 272-8516, Japan
Manuscript accepted for publication December 2, 2011
Short title: Immunological Insulin Resistance
doi: https://doi.org/10.4021/jem55w
| Letter to the Editor | ▴Top |
Anti-insulin antibody is sometimes observed in diabetic patients treated by exogenous insulin. Anti-insulin antibody induces immunological insulin resistance and poor glycemic control. We previously reported a type 1 diabetic patient who showed severe insulin resistance due to insulin analog aspart-induced anti-insulin antibody [1]. He has been treated by using insulin aspart and insulin glargine. We treated him with the use of the newest insulin analog, insulin glulisine. This treatment significantly ameliorated his glycemic control and anti-insulin antibody125I-binding rate, suggesting insulin glulisine as a possible treatment for other insulin analog-mediated immunological insulin resistance [1].
We also reported a type 2 diabetic patient (patient A) who developed severe insulin resistance due to anti-insulin antibody after 2 years of use of insulin lispro and insulin detemir [2]. Switching to the treatment with insulin glulisine and insulin glargine improved glycemic control, however, anti-insulin antibody binding rate was still high. Finally, three pre-meal injections of insulin glulisine and discontinuation of insulin glargine (4 weeks) decreased anti-insulin antibody 125I-binding rate [2].
Basal insulin therapy using long-acting insulin analogs may be necessary for type 1 diabetic patient or type 2 diabetic patients who have no endogenous insulin secretion capacity. How can we treat these patients with long-acting insulin analogs-mediated anti-insulin antibody?
Here, we will show the changes in HbA1c and anti-insulin antibody 125I-binding rate following the change in dose of insulin glulisine and insulin glargine in patient A (Fig. 1). Increased dose of insulin glulisine and 10 weeks-discontinuation of insulin glargine significantly decreased anti-insulin antibody 125I-binding rate, however, fasting blood glucose level (more than 200 mg/dl) and HbA1c level showed deterioration. After 10 weeks-discontinuation of insulin glargine, we re-started the use of low dose of insulin glargine. Fasting blood glucose and HbA1c levels were promptly decreased, and interestingly, anti-insulin antibody 125I-binding rate has been also continuously reduced.
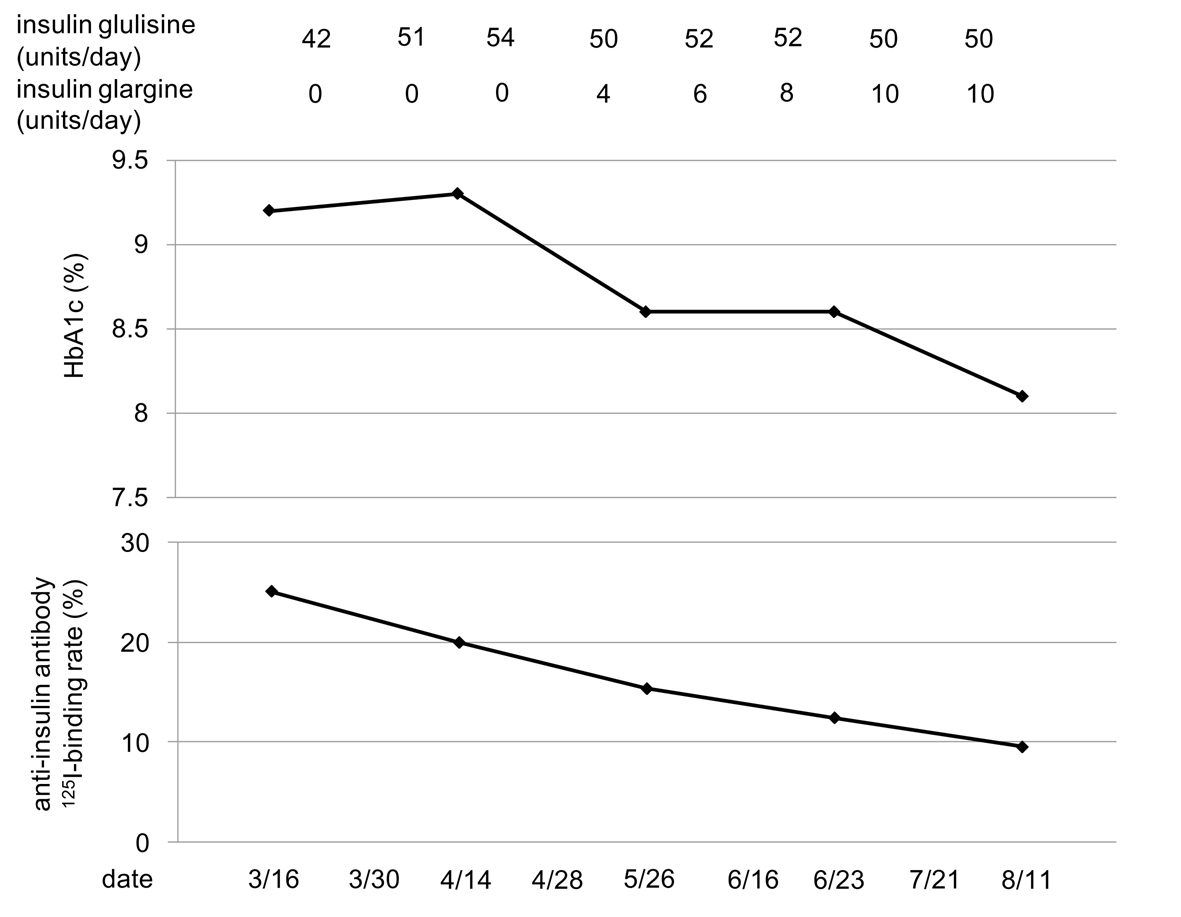 Click for large image | Figure 1. Changes in HbA1c and anti-insulin antibody125I-binding rate following the change in dose of insulin glulisine and insulin glargine in anti-insulin antibody-positive insulin-treated diabetic patient. |
As the treatments for anti-insulin antibody-mediated insulin resistance or hypoglycemia, in addition to our reports [1, 2], cessation of insulin administration [3], glucocorticoids [4], the combination therapy using glucocorticoids, immunosuppressant and plasmapheresis [5, 6], and insulin lispro [7, 8] have been reported (Table 1). Increasing dose of insulin glulisine and the use of low dose of insulin glargine after the discontinuation of insulin glargine for a sufficient long period may be a new treatment for the anti-insulin antibody-mediated immunological insulin resistance.
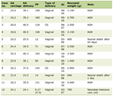 Click to view | Table 1. Reported Treatments for Anti-Insulin Antibody-Mediated Immunological Insulin Resistance and Hypoglycemia |
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Grant of National Center for Global Health and Medicine (22-120).
| References | ▴Top |
- Yanai H, Adachi H, Hamasaki H. Diabetic ketosis caused by the insulin analog aspart-induced anti-insulin antibody: successful treatment with the newest insulin analog glulisine. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(6):e108.
pubmed doi - Yanai H, Yoshimi T, Hamasaki H. Switching to three pre-meal injections of insulin glulisine from the basal-bolus insulin therapy improves glycemic control in a patient with type 2 diabetes who had anti-insulin antibody. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 2011.
doi - Hara K, Tobe K, Uchigata Y, Nakazono M, Yasuda K, Terauchi Y, Iwamoto Y, et al. Antibody-mediated insulin resistance treated by cessation of insulin administration. Intern Med. 2000;39(2):143-145.
pubmed doi - Suzuki K, Hirayama S, Ito S. A case of a non-insulin dependent diabetic patient with regular spontaneous hypoglycemic attacks, which were due to insulin-binding antibodies induced by human insulin therapy. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1997;182(2):163-173.
pubmed doi - Micic D, Brkic S, Kendereski A, Popovic V, Zoric S, Nikolic JA, Igrutinovic L, et al. Immunological resistance to human biosynthetic insulin—effects of immunosuppression and plasmapheresis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1993;19(1):83-89.
pubmed doi - Greenfield JR, Tuthill A, Soos MA, Semple RK, Halsall DJ, Chaudhry A, O'Rahilly S. Severe insulin resistance due to anti-insulin antibodies: response to plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy. Diabet Med. 2009;26(1):79-82.
pubmed doi - Honda M, Kawashima Y, Kawamura H, Fujikawa H, Kikuchi K, Ohashi H, Mori Y, et al. Acute liver dysfunction complicated with uncontrollable glycemia due to insulin antibody: successful treatment with glucocorticoid and lispro insulin. Intern Med. 2006;45(21):1225-1229.
pubmed doi - Lahtela JT, Knip M, Paul R, Antonen J, Salmi J. Severe antibody-mediated human insulin resistance: successful treatment with the insulin analog lispro. A case report. Diabetes Care. 1997;20(1):71-73.
pubmed doi
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism is published by Elmer Press Inc.
