| Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, ISSN 1923-2861 print, 1923-287X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Endocrinol Metab and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jofem.org |
Editorial
Volume 7, Number 1, February 2017, pages 1-4
Data Collection and the Questionnaires for the Effective Use of Biobank for Metabolic Disorders
Hidekatsu Yanaia, b, c, Yukari Takanob, Hiroki Adachia, Akiko Kawaguchia, Mariko Hakoshimaa, Yoko Waragaia, Tadanao Harigaea, Hidetaka Hamasakia, Hisayuki Katsuyamaa, Tomoko Kagab, Akahito Sakoa, b
aDepartment of Internal Medicine, National Center for Global Health and Medicine Kohnodai Hospital, Chiba, Japan
bClinical Research and Trial Center, National Center for Global Health and Medicine Kohnodai Hospital, Chiba, Japan
cCorresponding Author: Hidekatsu Yanai, Department of Internal Medicine, National Center for Global Health and Medicine Kohnodai Hospital, 1-7-1 Kohnodai, Ichikawa, Chiba 272-0034, Japan
Manuscript accepted for publication February 15, 2017
Short title: Editorial
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jem400w
Recently, the number of excellent original articles about genetics such as global transcript profiling and genetic ancestry has been increasing, due to that “Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism (JEM)” became widely known [1-3]. I wish further development of JEM as Editor-in-Chief. Here, we will introduce Biobank which may induce further development of studies on genetics, endocrinology and metabolism, and will also show the questionnaires for the effective use of Biobank for metabolic disorders.
The idea for Biobank began in 1998 when UK government spending review gave the Medical Research Council additional funds to set up “nationally available DNA collections” [4]. We started to set up the Biobank for Metabolic Disorders in the National Center for Global Health and Medicine Kohnodai Hospital with financial support from the Biobank Fund of National Center for Global Health and Medicine. The Biobank project is a prospective cohort study to collect baseline data and blood samples from individuals who will be followed up, to find the correlation of disease with genetic, environmental exposure, and baseline data [4]. When disease developed, prospectively collected samples linked to baseline data and baseline data themselves can be used to look back for evidence of exposure [4].
Genetic and environmental factors are associated with development of metabolic disorders. Genetic factors may modify the influences of environmental factors, and environmental factors including lifestyle-related behaviors may also enhance or reduce the effects of genetic factors, which may be further modified by gender and aging [5]. To understand the pathogenesis of metabolic disorders, Biobank may be a useful tool.
In our Biobank, informed consent (IC) is obtained after the explanation of Biobank. After IC was obtained, we collected the baseline data using the questionnaires about diabetes-related and other health-related factors, lifestyle including eating behaviors [6]. At the first visit after the obtainment of IC, DNA and serum are obtained from patients. Serum and medical records including laboratory data, body weight, blood pressure and medication are obtained at every visit.
We believe that the obtainment of valid and abundant baseline data is essential to make the useful Biobank for metabolic disorders.
Here, we will introduce our questionnaires to obtain diabetes-related data (Table 1), other health-related data (Table 2) and the data about lifestyle (Table 3), which may help you study the metabolic disorders. We will be happy that our questionnaires lead your study to success.
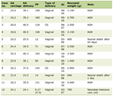 Click to view | Table 1. Diabetes-Related Data |
 Click to view | Table 2. Other Health-Related Data |
 Click to view | Table 3. The Data About Lifestyle |
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest concerning this article.
Funding Sources
This work was funded by a research grant from the Biobank Fund of National Center for Global Health and Medicine.
| References | ▴Top |
- Doumatey AP, Xu H, Huang H, Trivedi NS, Lei L, Elkahloun A, Adeyemo A, et al. Global Gene Expression Profiling in Omental Adipose Tissue of Morbidly Obese Diabetic African Americans. J Endocrinol Metab. 2015;5(3):199-210.
doi pubmed - Luk HM. Clinical and Genetic Study of Pseudohypoparathyroidism Type 1b in Hong Kong Chinese. J Endocrinol Metab. 2016;6(2):64-70.
doi - de Queiroz EM, Barbosa PO, Candido AP, Castro IM, Machado-Coelho GLL, Leite TM, Pereira RW, de Freitas RN. Genetic Ancestry Is Associated With Systolic Blood Pressure and Glucose in Brazilian Children and Adolescents. J Endocrinol Metab. 2016;6(6):167-171.
doi - Barbour V. UK Biobank: a project in search of a protocol? Lancet. 2003;361(9370):1734-1738.
doi - Yanai H. The Metabolic Disorder and Metabolic Disorder-Related Diseases Model. J Endocrinol Metab. 2016;6(6):165-166.
doi - Yoshimatsu H. [Behavioral therapy for obesity]. Nihon Rinsho. 2009;67(2):373-383.
pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism is published by Elmer Press Inc.
