| Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, ISSN 1923-2861 print, 1923-287X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Endocrinol Metab and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jofem.org |
Case Report
Volume 5, Number 3, June 2015, pages 224-225
Olfactory Sulcus Hypoplasia Images of a Case With Kallmann Syndrome
Banu Pinar Sarer Yureklia, d, Nilufer Ozdemir Kutbaya, Omer Kitisb, Ferda Ozkinayc, Fusun Saygilia
aEndocrinology and Metabolism Department, Ege University Faculty of Medicine, Izmir, Turkey
bRadiology Department, Ege University Faculty of Medicine, Izmir, Turkey
cMedical Genetics Department, Ege University Faculty of Medicine, Izmir, Turkey
dCorresponding Author: Banu Sarer Yurekli, Department of Endocrinology, Ege University Faculty of Medicine, Bornova 35100, Izmir, Turkey
Manuscript accepted for publication June 24, 2015
Short title: Olfactory Sulcus Hypoplasia
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.14740/jem279w
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Kallmann syndrome is a form of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism accompanied by anosmia or hyposmia. MR images of midline defects in Kallmann syndrome were rarely seen in the literature. We wanted to put emphasis on the midline developmental defects accompanied to Kallmann syndrome shown by MR images of olfactory sulcus hypoplasia.
Keywords: Olfactory sulcus hypoplasia; Kallmann syndrome; Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Kallmann syndrome is a form of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism accompanied by anosmia or hyposmia. It is transmitted genetically as autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive and X-linked. Several gene mutations are identified. Herein, we present our case of Kallmann syndrome.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
A 22-year-old male patient was admitted to the outpatient clinic with the complaint of absence of facial hair. He also had complaints of erectile dysfunction, decrease in libido and disability to smell. Physical examination results were as follows: height: 177 cm, weight: 60.5 kg, BMI: 19.15 kg/m2, arm length: 187 cm, and penile length: 3 - 4 cm. Right testicular volume was 1 cc, and left testicular volume was 0.6 cc. His epiphyseal plates were currently open and his bone age was 15 years. Laboratory examination results were as follows: FSH: 0.27 mIU/mL, LH: 0.1 mIU/mL, t. testosterone: 0.25 ng/dL, and TSH: 1.63 µIU/mL. Kallmann syndrome was diagnosed with regard to hypogonadism together with anosmia. KAL1 gene mutation was not detected. On craniofacial MRI, left olfactory sulcus was significantly shallow and gyrus rectus was hypoplastic. Bilateral olfactory sulci in a case without Kallmann syndrome were thicker (Fig. 1) compared to those of our case with the syndrome (Fig. 2). Human chorionic gonadotrophin was given for 6 months; after that, testosterone hormone replacement was started. His symptoms were relieved with hormone replacement.
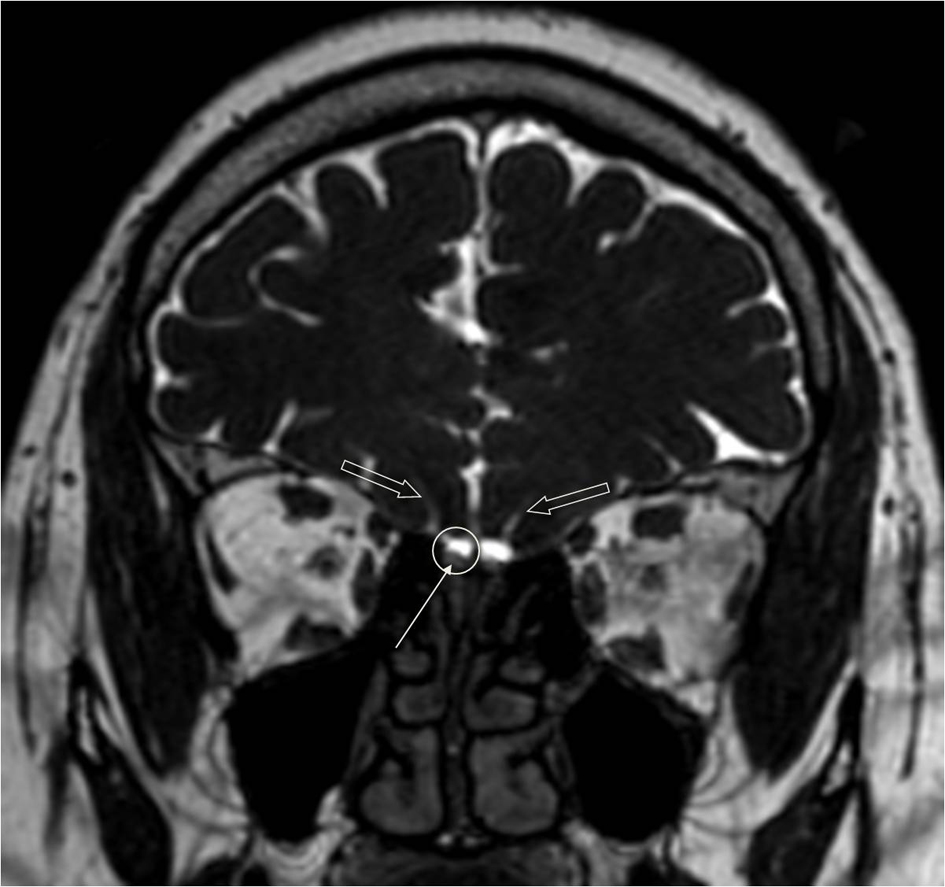 Click for large image | Figure 1. Coronal T2 image of a subject without Kallmann syndrome: bilateral olfactory sulci (light arrows), olfactory groove (circle), and olfactory bulbi inside olfactory groove (arrow). |
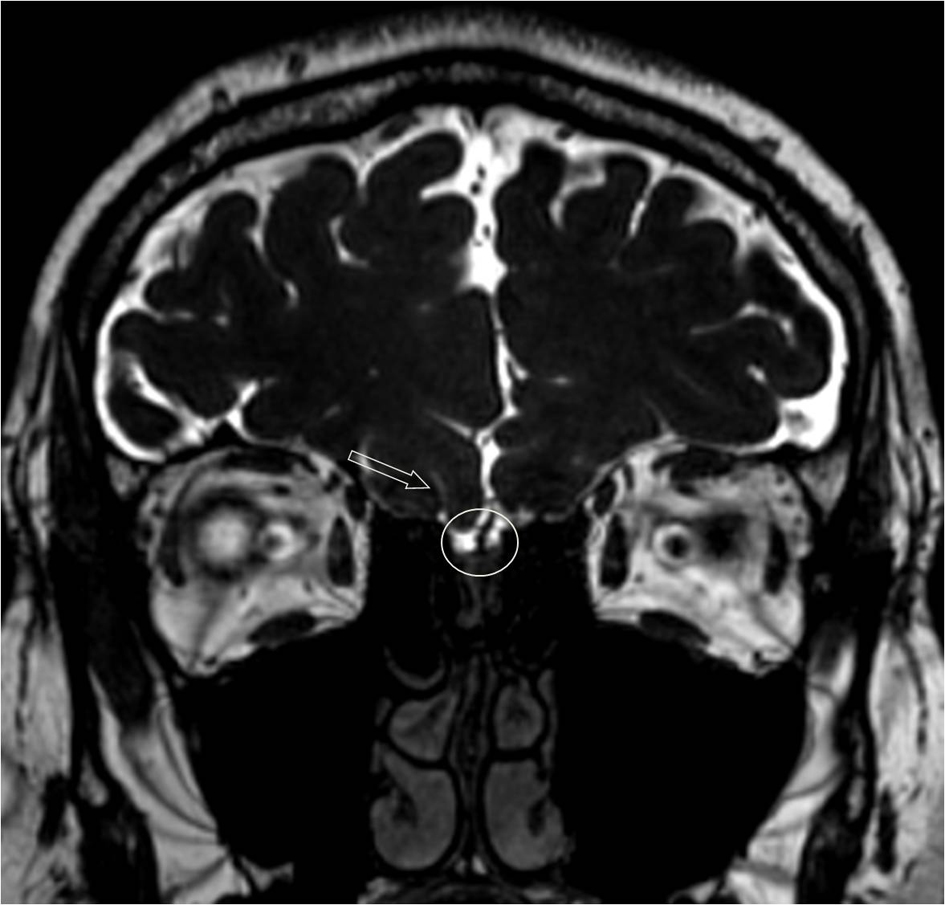 Click for large image | Figure 2. Coronal T2 image of the case with Kallmann syndrome. Normal olfactory sulcus was at the right (light arrow), olfactory sulcus was not seen on the left. Olfactory grooves were narrower on the left (circle), and olfactory bulbi were thinner compared to the MRI of the subject without Kallmann syndrome. |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
Co-occurrence of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism with anosmia was first defined in 1944 by Kallmann and his colleagues. Prevalence of Kallmann syndrome was 1/10,000 in females and 1/15,000 in males [1, 2]. Association of hypogonadism with anosmia is due to developmental defects in rhinencephalon. In addition to KAL-1 gene mutation, FGFR-1, FGF8, prokineticin (PROK2) and its receptor (PROK2R) mutations were also defined. MR images of midline defects in Kallmann syndrome were rarely seen in the literature. We wanted to put emphasis on the midline developmental defects accompanied to Kallmann syndrome shown by MR images of olfactory sulcus hypoplasia.
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
| References | ▴Top |
- Vogl TJ, Stemmler J, Heye B, Schopohl J, Danek A, Bergman C, Balzer JO, et al. Kallman syndrome versus idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism at MR imaging. Radiology. 1994;191(1):53-57.
doi pubmed - Moorman JR, Crain B, Osborne D. Kallman's syndrome with associated cardiovascular and intracranial anomalies. Am J Med. 1984;77(2):369-372.
doi
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism is published by Elmer Press Inc.
