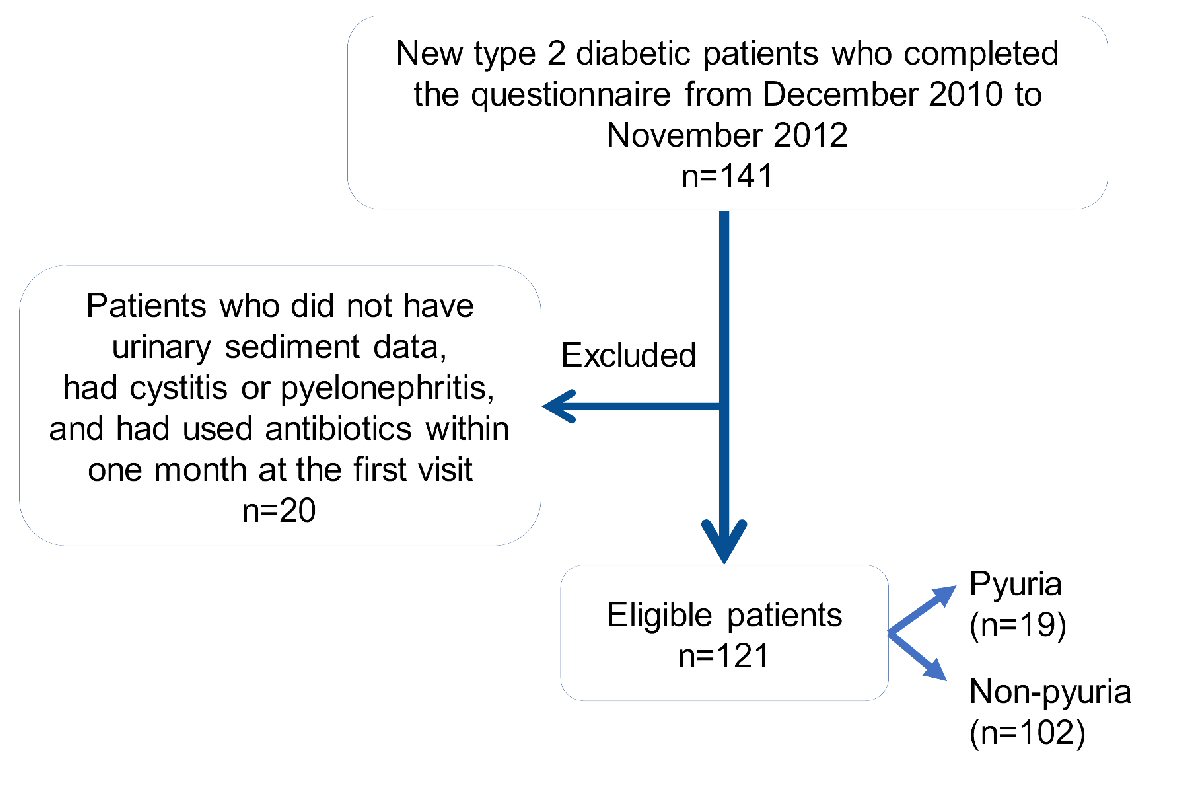
Figure 1. The recruitment of studied subjects.
| Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, ISSN 1923-2861 print, 1923-287X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Endocrinol Metab and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jofem.org |
Original Article
Volume 9, Number 6, December 2019, pages 193-198
The Risk Factors for Asymptomatic Pyuria Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Figures

Tables
| BMI: body mass index; HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c; HPF: high-power field. | |
| Gender (male/female) | 69/52 |
| Age (year) | 63.2 ± 13.4 |
| Weight (kg) | 67.0 ± 16.2 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.0 ± 5.7 |
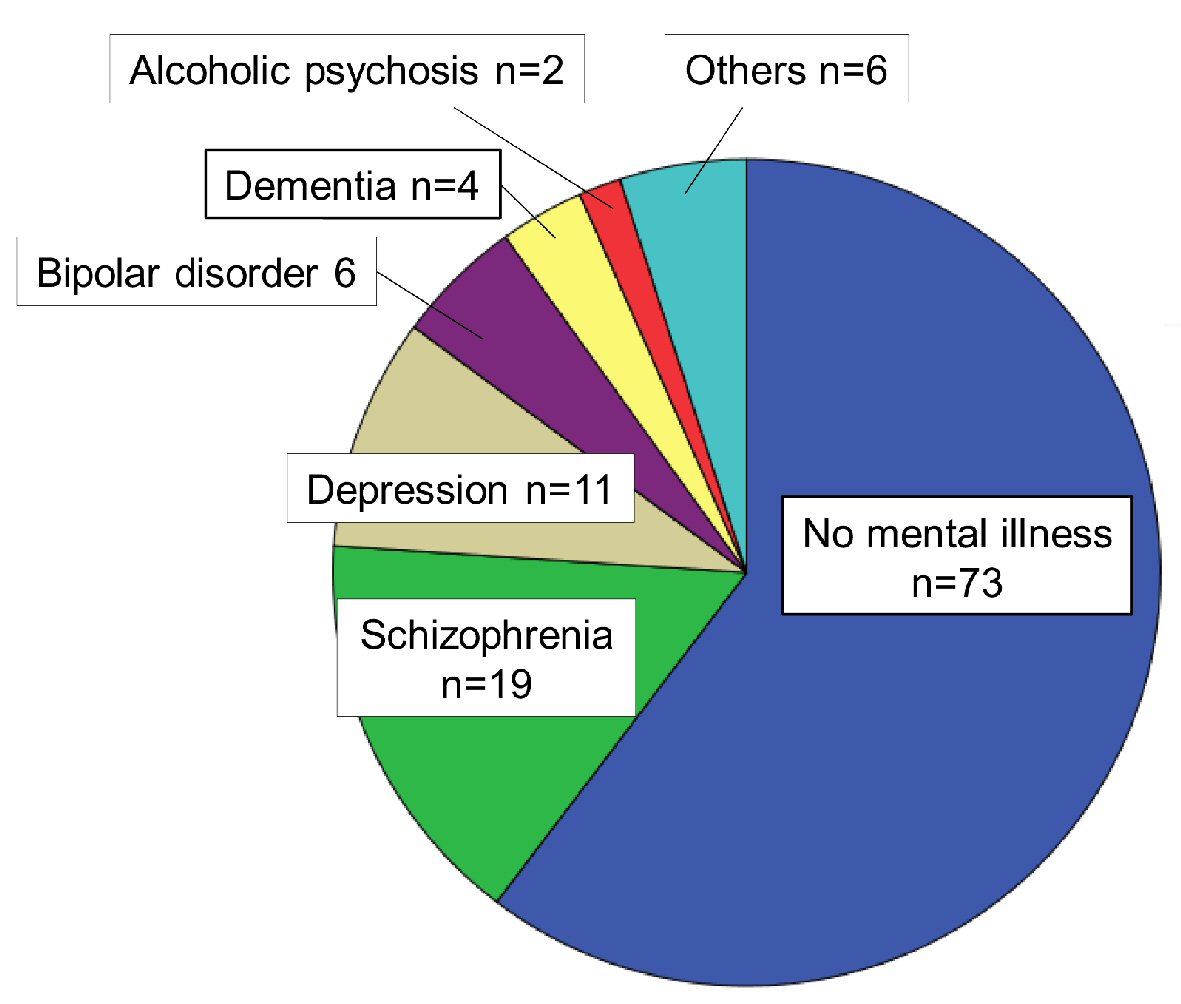
| Mental illness (n) | 48 |
| Duration of diabetes (year) | 5.1 ± 7.5 |
| HbA1c (%) | 8.5 ± 2.1 |
| Plasma glucose (mg/dL) | 197 ± 95 |
| Urine leukocytes (/HPF) | |
| < 1 | 66 |
| 1 - 4 | 25 |
| 5 - 9 | 11 |
| 10 - 29 | 11 |
| 30 - 49 | 4 |
| 50 - 99 | 3 |
| ≥ 100 | 1 |
| Total | 121 |
| Non-pyuria (n = 102) | Pyuria (n = 19) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMI: body mass index. | |||
| Age (year) | 62.8 ± 12.7 | 65.1 ± 17.2 | 0.60 |
| ≥ 65 years old (%) | 51.0 | 63.2 | 0.33 |
| Female (%) | 35.3 | 84.2 | < 0.01 |
| Weight (kg) | 67.3 ± 16.4 | 65.3 ± 15.5 | 0.62 |
| Waist circumference (cm) (n = 99) | 92.1 | 96.1 | 0.32 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.6 ± 5.6 | 27.7 ± 6.2 | 0.16 |
| Mental illness (%) | 35.3 | 63.2 | 0.02 |
| Taking psychotropic drugs (%) | 33.3 | 57.9 | 0.04 |
| Duration of mental illness (year) | 17.7 ± 14.3 | 16.9 ± 17.0 | 0.85 |
| Non-pyuria (n = 102) | Pyuria (n = 19) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVR-R: coefficient of variations of R-R intervals. | |||
| Duration of diabetes (year) | 5.3 ± 7.6 | 4.0 ± 7.2 | 0.483 |
| Numbness (%) | 19.6 | 21.1 | 0.309 |
| CVR-R (%) (n = 79) | 3.2 ± 2.0 (n = 67) | 1.8 ± 1.1 (n = 12) | 0.002 |
| CVR-R ≥ 2% (%) | 67.2 (n = 45) | 33.3 (n = 4) | 0.049 |
| CVR-R < 2% (%) | 32.8 (n = 22) | 66.7 (n = 8) | 0.049 |
| Use of laxatives (%) | 9.8 | 21.1 | 0.232 |
| Retinopathy (%) (n = 74) | 13.7 | 10.5 | 0.703 |
| Non-pyuria (n = 102) | Pyuria (n = 19) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cre: creatinine; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; BUN: blood urea nitrogen; HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c. | |||
| eGFR (mL/min) | 82.1 ± 21.8 | 72.6 ± 25.7 | 0.10 |
| Cre (mg/dL) | 0.72 ± 0.17 | 0.74 ± 0.3 | 0.67 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 14.6 ± 5.3 | 14.5 ± 5.0 | 0.92 |
| Proteinuria (%) | 16.7 | 31.6 | 0.20 |
| Glucosuria (%) | 42.2 | 42.1 | 1.00 |
| Plasma glucose (mg/dL) | 199 ± 100 | 190 ± 63 | 0.70 |
| HbA1c (%) (n = 120) | 8.5 ± 2.2 | 8.4 ± 1.5 | 0.80 |
| Non-pyuria (n = 36) | Pyuria (n = 16) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVR-R: coefficient of variations of R-R intervals. | |||
| Mental illness (%) | 36.1 | 75.0 | 0.01 |
| CVR-R < 2% (%) | 18.2 | 72.7 | < 0.01 |
| CVR-R (%) | 3.5 | 1.5 | < 0.01 |
| Non-mental illness (n = 73) | Mood disorder (n = 17) | Schizophrenia (n = 19) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI: body mass index. | ||||
| Pyuria (%) | 9.6 | 11.8 | 21.1 | 0.36 |
| Age (year) | 66.1 ± 10.9 | 58.7 ± 16.5 | 56.1 ± 15.1 | < 0.01 |
| ≥ 65 years old (%) | 56.2 | 52.9 | 42.1 | 0.55 |
| Female (%) | 37.0 | 47.1 | 47.4 | 0.59 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.5 ± 4.2 | 28.4 ± 7.8 | 30.3 ± 6.7 | < 0.01 |
| Non-mental illness (n = 73) | Mood disorder (n = 17) | Schizophrenia (n = 19) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVR-R: coefficient of variations of R-R intervals; HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c. | ||||
| CVR-R (%) (n = 60) | 3.1 ± 2.1 | 2.8 ± 1.9 | 3.6 ± 2.2 | 0.71 |
| Use of laxatives (%) | 4.1 | 11.8 | 26.3 | 0.01 |
| Retinopathy (%) (n = 74) | 11 | 23.5 | 10.5 | 0.72 |
| Glucosuria (%) | 41.7 | 29.4 | 57.9 | 0.22 |
| Plasma glucose (mg/dL) | 198 ± 92 | 203 ± 132 | 207 ± 79 | 0.93 |
| HbA1c (%) | 8.6 ± 2.1 | 8.8 ± 2.5 | 8.5 ± 2.0 | 0.92 |
| Studies | Nakano et al, [2] | Ozdem et al, [3] | Present study |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVR-R: coefficient of variations of R-R intervals; HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c. | |||
| Publication (year) | 2001 | 2006 | 2019 |
| Mean age (years) | 64.8 | 60.1 | 63.2 |
| HbA1c (%) | 8.6 | 9.1 | 8.5 |
| Duration of diabetes (years) | 10.0 | 7.9 | 5.1 |
| Prevalence of pyuria (%) | |||
| Non-diabetic males | - | 3.4 | - |
| Non-diabetic females | 15.8 | 8.7 | - |
| Diabetic males | - | 12.2 | 4.3 |
| Diabetic females | 27.9 | 21.4 | 30.8 |
| Risk factors | Older age, diabetes, retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy, history of macroangiopathy, longer duration of diabetes | Diabetes, female | Mental illness, female, lower CVR-R |