| Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, ISSN 1923-2861 print, 1923-287X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Endocrinol Metab and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jofem.org |
Editorial
Volume 6, Number 6, December 2016, pages 165-166
The Metabolic Disorder and Metabolic Disorder-Related Diseases Model
Hidekatsu Yanai
Department of Internal Medicine, National Center for Global Health and Medicine Kohnodai Hospital, 1-7-1 Kohnodai, Ichikawa, Chiba 272-0034, Japan
Manuscript accepted for publication December 07, 2016
Short title: Editorial
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jem387w
In this issue (J Endocrinol Metab, December 2016, p167), Queiroz et al report a significant association of African ancestry with higher systolic blood pressure and blood glucose as compared with European ancestry among Brazilian children and adolescents [1], suggesting a significant effect of genetic factor on blood pressure and blood glucose by using admixed populations. Their study made me think about “The metabolic disorder and metabolic disorder-related diseases model”.
In the study which assessed the development of body mass and examine the role of race or ethnicity, sex, and birth year in obesity onset in young US adults, using the National Longitudinal Survey of Youth 1979, obesity onset was 2.1 (95% CI: 1.6 - 2.7) times faster for black women and 1.5 (CI: 1.1 - 2.0) times faster for Hispanic women than for white women [2]. The pattern for men differed: obesity developed most rapidly in Hispanic men, but relative rates of obesity onset for white men compared with black men varied according to age, suggesting a significant influence of gender and aging on genetic and environmental factors.
According to analysis of data on 8,814 men and women aged 20 years or older from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1988 - 1994), Mexican Americans had the highest age-adjusted prevalence of the metabolic syndrome (31.9%) [3]. Among African Americans, women had about a 57% higher prevalence than men, and among Mexican Americans, women had about a 26% higher prevalence than men, indicating a significant difference in genetic effect between sexes.
Compared with African-American children, Caucasian children have significantly greater visceral fat even after adjusting for total fat. However, African-American children showed more insulin resistance, independent of visceral fat accumulation [4, 5], suggesting that adverse metabolic effects by visceral obesity may differ according to race/ethnicity.
I will show “The metabolic disorder and metabolic disorder-related diseases model” in Figure 1. Genetic and environmental factors are associated with development of metabolic disorder and metabolic disorder-related diseases. Genetic factors may modify the influences of environmental factors, and environmental factors including socio-economic status, lifestyle-related behaviors and educational status may also enhance or reduce the effects of genetic factors, which may be further modified by gender and aging.
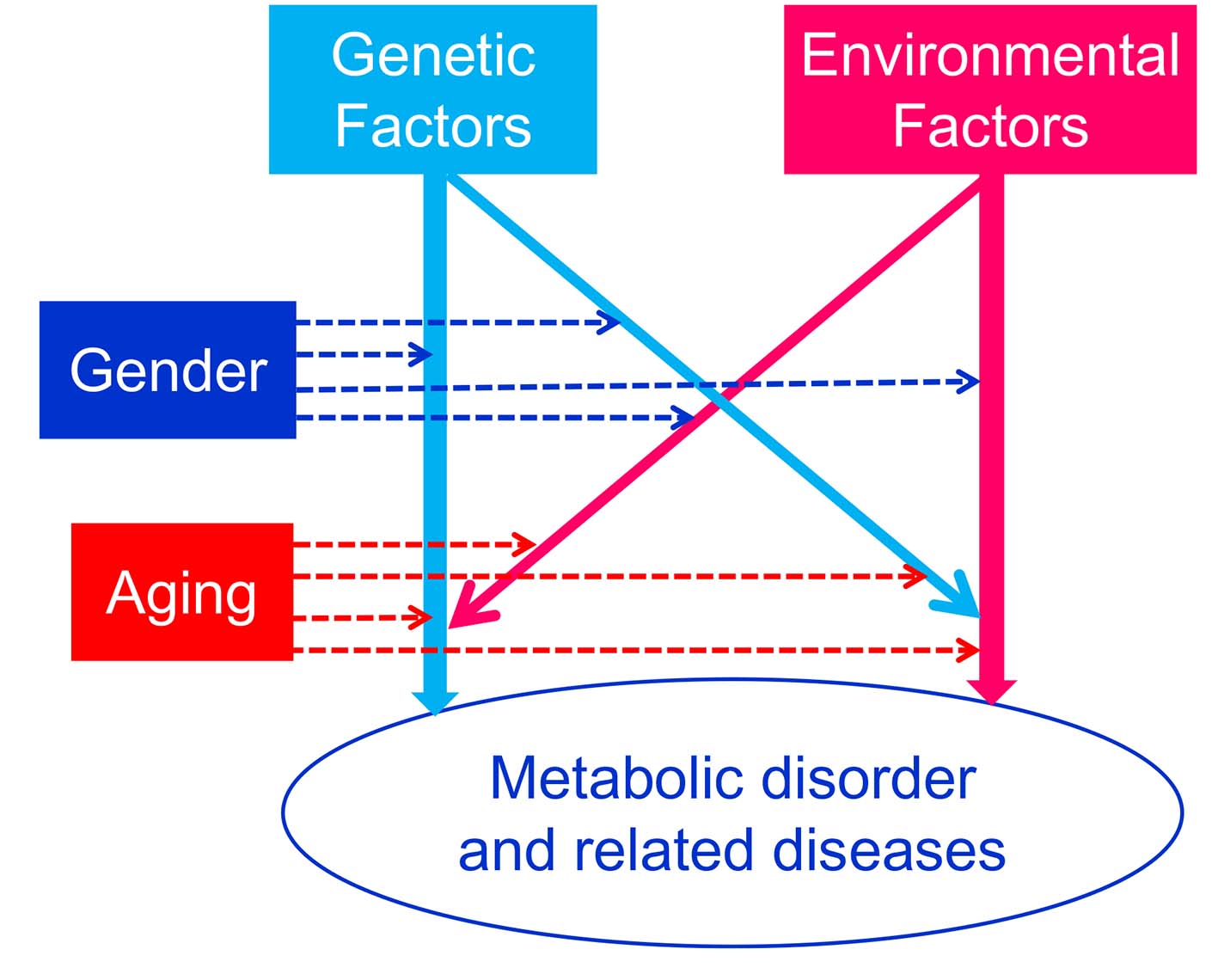 Click for large image | Figure 1. The metabolic disorder and metabolic disorder-related diseases model. |
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest concerning this article.
| References | ▴Top |
- Queiroz EM, Barbosa PO, Candido AP, Castro IM, Machado-Coelho GL, Leite TM, et al. Genetic ancestry is associated with systolic blood pressure and glucose in Brazilian children and adolescents. J Endocrinol Metab. 2016;6(6):167-171.
- McTigue KM, Garrett JM, Popkin BM. The natural history of the development of obesity in a cohort of young U.S. adults between 1981 and 1998. Ann Intern Med. 2002;136(12):857-864.
- Ford ES, Giles WH, Dietz WH. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among US adults: findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. JAMA. 2002;287(3):356-359.
- Gower BA, Nagy TR, Goran MI. Visceral fat, insulin sensitivity, and lipids in prepubertal children. Diabetes. 1999;48(8):1515-1521.
- Goran MI, Nagy TR, Treuth MS, Trowbridge C, Dezenberg C, McGloin A, Gower BA. Visceral fat in white and African American prepubertal children. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997;65(6):1703-1708.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism is published by Elmer Press Inc.