| Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, ISSN 1923-2861 print, 1923-287X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Endocrinol Metab and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jofem.org |
Letter to the Editor
Volume 3, Number 3, June 2013, pages 78-80
Effects of Sitagliptin May Depend on Clinical and Laboratory Data at the Baseline
Hidekatsu Yanaia, b, c
aDepartment of Internal Medicine, National Center for Global Health and Medicine, Kohnodai Hospital, Chiba 272-8516, Japan
bClinical Research Center, National Center for Global Health and Medicine, Kohnodai Hospital, Chiba 272-8516, Japan
cCorresponding author: Hidekatsu Yanai, Department of Internal Medicine and Clinical Research Center, National Center for Global Health and Medicine, Kohnodai Hospital, 1-7-1 Kohnodai, Chiba 272-8516, Japan
Manuscript accepted for publication June 12, 2013
Short title: Effects of Sitagliptin
doi: https://doi.org/10.4021/jem171w
| To the Editor | ▴Top |
We have previously reported that the 6-month sitagliptin treatment significantly reduced HbA1c, body weight in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes [1]. We also found a negative correlation between changes in body weight and body mass index (BMI) at baseline, and also reported a negative correlation between changes in HbA1c and HbA1c levels at baseline [1].
Kubota A et al reported that the 12 weeks-sitagliptin treatment significantly decreased HbA1c, serum total cholesterol and postprandial triglyceride levels, systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure, and also increased serum creatinine [2]. However, we could not observe significant differences in systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and serum lipid levels, and estimated glomerular filtration rate (e-GFR) between before and after the sitagliptin treatment [1].
The mean ± SD of age (63.3 ± 11.5) in the study by Kubota A et al was younger than that (64.0 ± 14.0) in our study [1, 2]. Aging influences pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. To understand how age influences effects of sitaglitpin, we analyzed data by dividing subjects studied into patients who are 75 years old or older (the elderly group, n = 54) and patients who are 74 years old or younger (the young group, n = 166). Age ranged from 22 to 74 years old and from 75 to 91 years old, and 83 and 32 female patients were included in the young group and the elderly group, respectively. The mean ± SD of age and BMI were 58.0 ± 12.0 years old and 27.0 ± 5.4 kg/m2, and 81.0 ± 5.0 years old and 23.2 ± 4.0 kg/m2 in the young group and the elderly group, respectively. In the young group, sitagliptin significantly reduced plasma glucose levels in addition to reduction in body weight and HbA1c which were observed in the previous study (Table 1) [1]. In the elderly group, sitaglitpin significantly reduced HbA1c, however, did not show a significant reduction of body weight which was observed in the previous study (Table 2) [1].
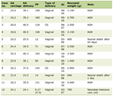 Click to view | Table 1. Clinical and Biochemical Data Before and After 6 Month-Use of Sitagliptin in 166 People Who are 74 Years Old or Younger |
 Click to view | Table 2. Clinical and Biochemical Data Before and After 6 Month-Use of Sitagliptin in 54 People Who are 75 Years Old or Older |
Differences in changes in clinical and biochemical data after 6 month-use of sitagliptin between the young group and the elderly group were shown in Table 3. Sitagliptin showed greater decrease of body weight, systolic blood pressure, plasma glucose and HbA1c, and also showed smaller decrease of serum levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and e-GFR in the young group as compared with the elderly group.
 Click to view | Table 3. Differences in Changes in Clinical and Biochemical Data After 6 Month-Use of Sitagliptin Between People Who are 74 Years Old or Younger and People Who are 75 Years Old or Older |
In conclusion, our previous study and present study demonstrated that effects of sitagliptin may depend on clinical data such as age and BMI and laboratory data such as HbA1c at the baseline.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Tomoko Kaga, Yukari Takano, Fumi Kawasaki, Yukie Kawamura, and Naomi Inoue at Clinical Research Center, National Center for Global Health and Medicine Kohnodai Hospital, for their technical help. This work was supported by the Grant of National Center for Global Health and Medicine (22-120).
| References | ▴Top |
- Yanai H, Adachi H, Hamasaki H, Masui Y, Yoshikawa R, Moriyama S, Mishima S, et al. Effects of 6-month sitagliptin treatment on glucose and lipid metabolism, blood pressure, body weight and renal function in type 2 diabetic patients: a chart-based analysis. J Clin Med Res. 2012;4(4):251-258.
pubmed - Kubota A, Maeda H, Kanamori A, Matoba K, Jin Y, Minagawa F, Obana M, et al. Pleiotropic effects of sitagliptin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. J Clin Med Res. 2012;4(5):309-313.
pubmed
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism is published by Elmer Press Inc.